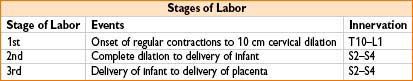
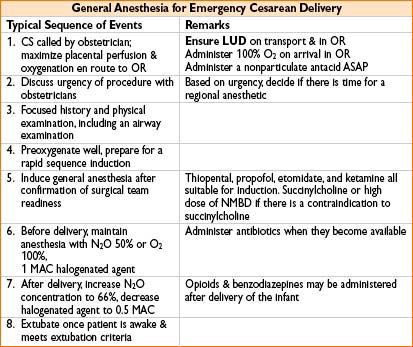
ANESTHESIA FOR LABOR AND DELIVERY
• Nonpharmacologic analgesia choices: Hypnotherapy, hydrotherapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
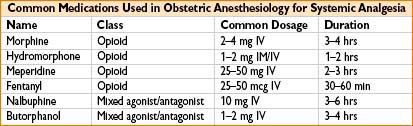
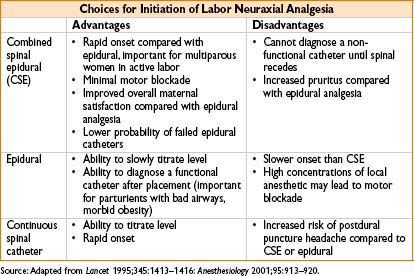
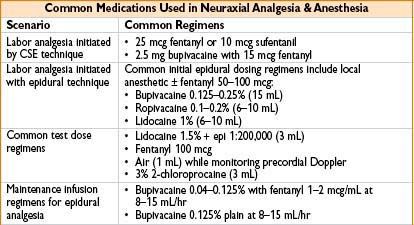
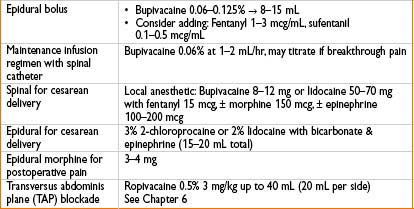
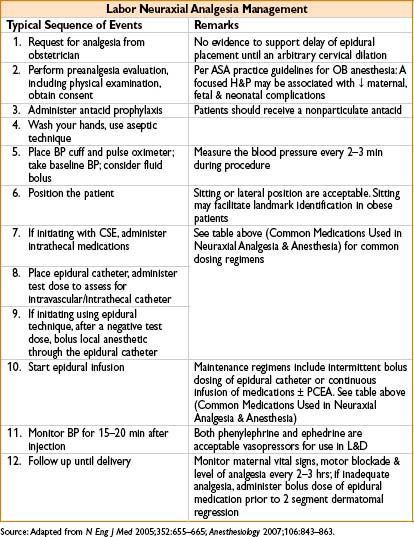
• Pharmacologic analgesia: Inhalation analgesia, parenteral opioid analgesia (fentanyl, nalbuphine), pudendal block, paracervical block, neuraxial analgesia. Of these, epidural & combined spinal-epidural (CSE) analgesia are most effective
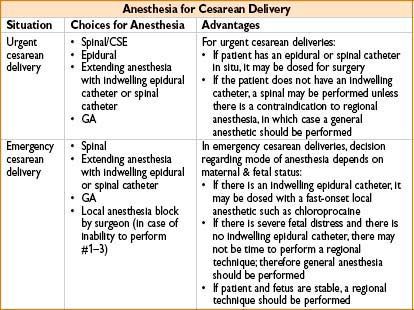








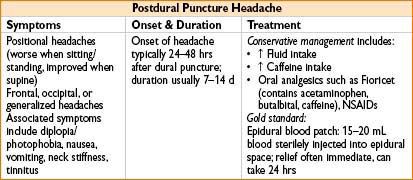
POSTDURAL PUNCTURE HEADACHE (PDPH)
Differential dx: Nonspecific headache, migraines, lactation headaches, cortical vein thrombosis, meningitis, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage
H&P and +/- neuroimaging necessary for correct diagnosis
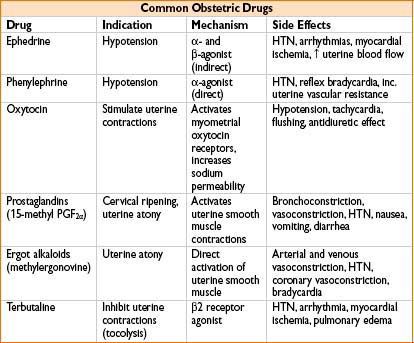
DRUGS USED IN OBSTETRIC SURGERY
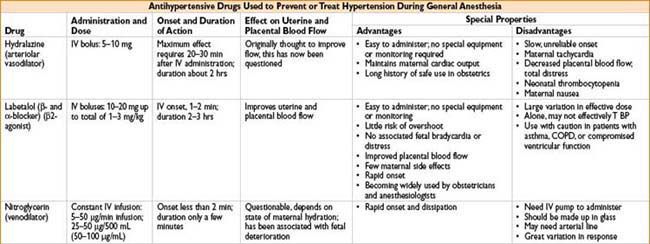
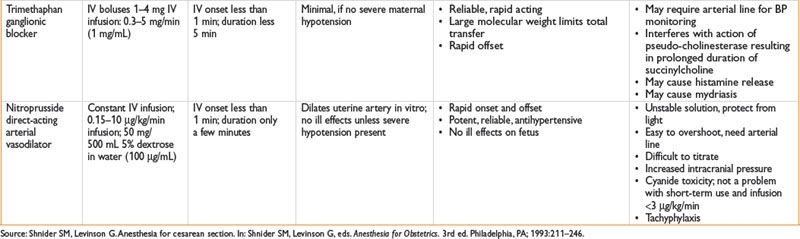
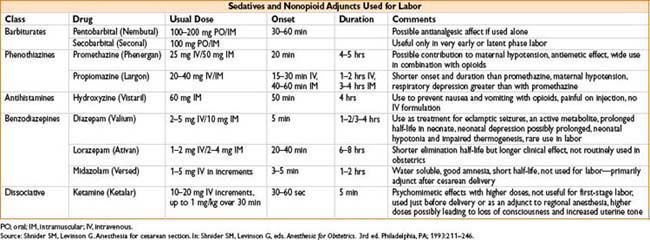
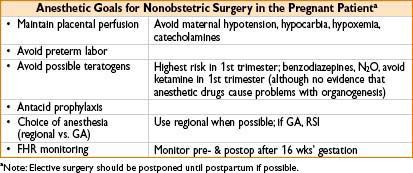
INTRAPARTUM FETAL ASSESSMENT AND THERAPY
UTEROPLACENTAL BLOOD FLOW
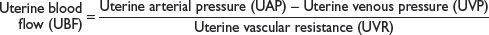
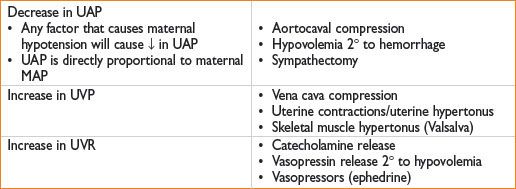
Factors That Decrease Uterine Blood Flow
PLACENTAL TRANSFER OF MEDICATIONS
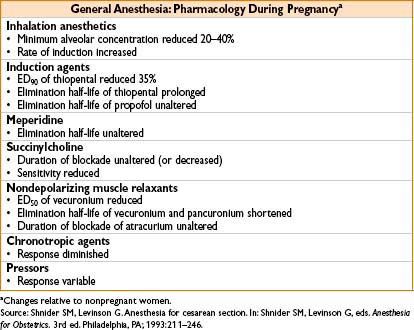
Inhalational & IV induction agents, local anesthetics → can cross placenta
• However, bupivacaine highly protein-bound & chloroprocaine highly metabolized (fetal conc. of these drugs lower than when lidocaine is used)

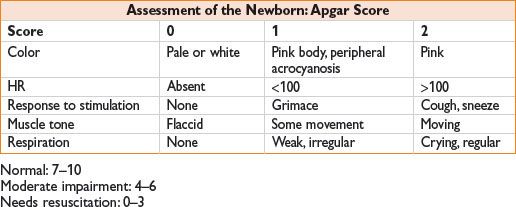
APGAR SCORE
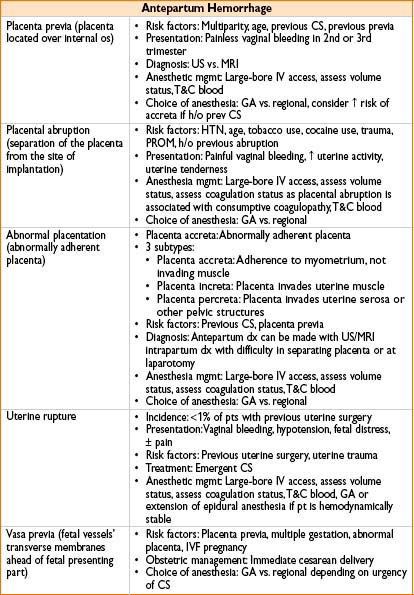
ANTEPARTUM HEMORRAGE
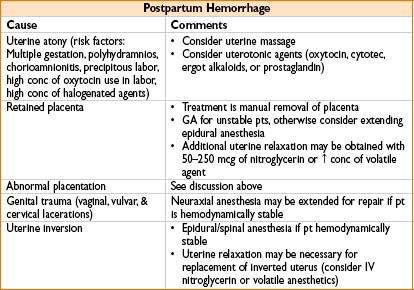
POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE
• Incidence: 10% of all deliveries
• Definition: 500 mL EBL in vaginal delivery, 1,000 mL EBL for CS
• Anesthetic management:
→ Assess pt volume status, hemoglobin & coagulation status, IV access
→ Send T&S or type & crossmatch for blood
→ Administer IV fluid, blood, & vasopressors as indicated
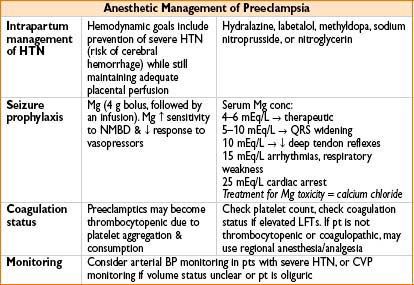
HYPERTENSIVE DISORDERS OF PREGNANCY
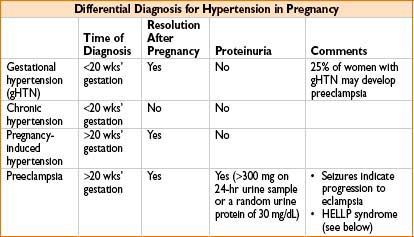
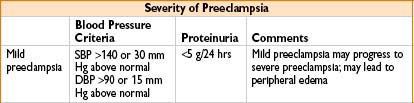
Preeclampsia
• Definition: Hypertension + proteinuria after 20 wks’ gestation
• Pathophysiology: Exact mechanism unknown, may involve imbalance between prostaglandins (thromboxane A & prostacyclin), abnl sensitivity to catecholamines, or antigen–antibody reactions between fetal & maternal tissues
• Treatment: Only definitive cure for preeclampsia is delivery of the infant


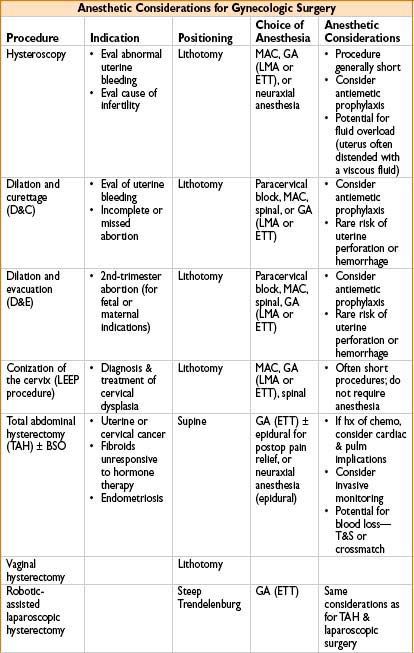
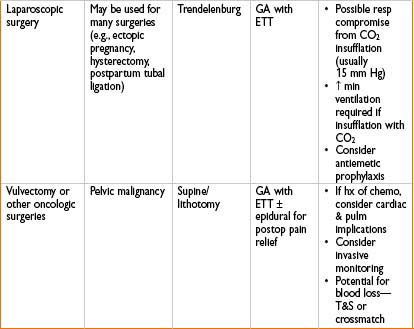
ANESTHESIA FOR GYNECOLOGIC SURGERY
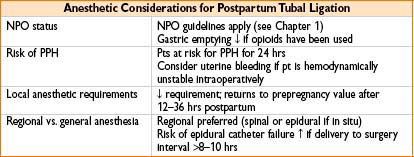
Postpartum Tubal Ligation (PPTL)
• Benefits of immediate PPTL include
• Ease of access to fallopian tubes (uterus & ovaries are out of pelvis)
• ↓ risk of bowel laceration, vascular injury
• ↓ duration of hospital stay, ↓ cost (compared to outpatient procedure)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>









