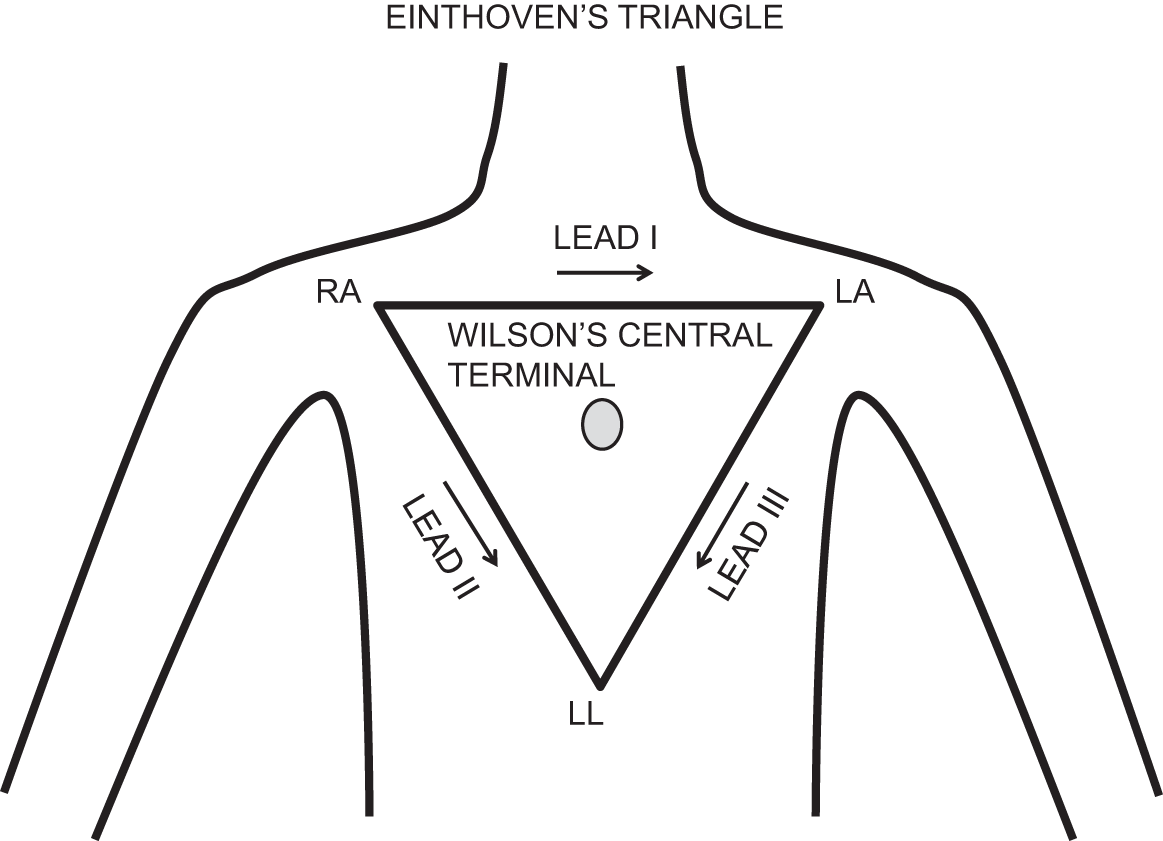
Cardiac impulses begin in the right atrium at the sino-atrial node. The wave of depolarisation spreads through both atria to the atrioventricular node. Here it travels via the bundle of His and Purkinje fibres to innervate the ventricular muscle. The general direction of depolarisation forms the cardiac axis.
Deflections of the ECG depend on the position of the electrode in relation to the direction of depolarisation. Positive deflections indicate depolarisation moving towards the electrode; leads that lie parallel to the cardiac axis have predominantly positive QRS complexes (e.g. lead II). Negative deflections indicate depolarisation moving away from the electrode.
Applied science
How is the ECG used in anaesthetic practice?
The ECG is regarded as an essential monitor during anaesthesia. It provides vital information such as heart rate and rhythm, and can indicate myocardial ischaemia.
High- and low-pass filters can be selected for use with the ECG depending on the intended use. In diagnostic mode, where a greater diagnostic accuracy for ST segments is required, the high-pass filter is set at 0.05 Hz and the low-pass filter at 40, 100 or 150 Hz. For routine rhythm monitoring during anaesthesia, where noise can be problematic, a more filtered monitoring mode is used. In monitoring mode, the high-pass filter is set higher to 0.5 Hz and the low-pass filter at 40 Hz.
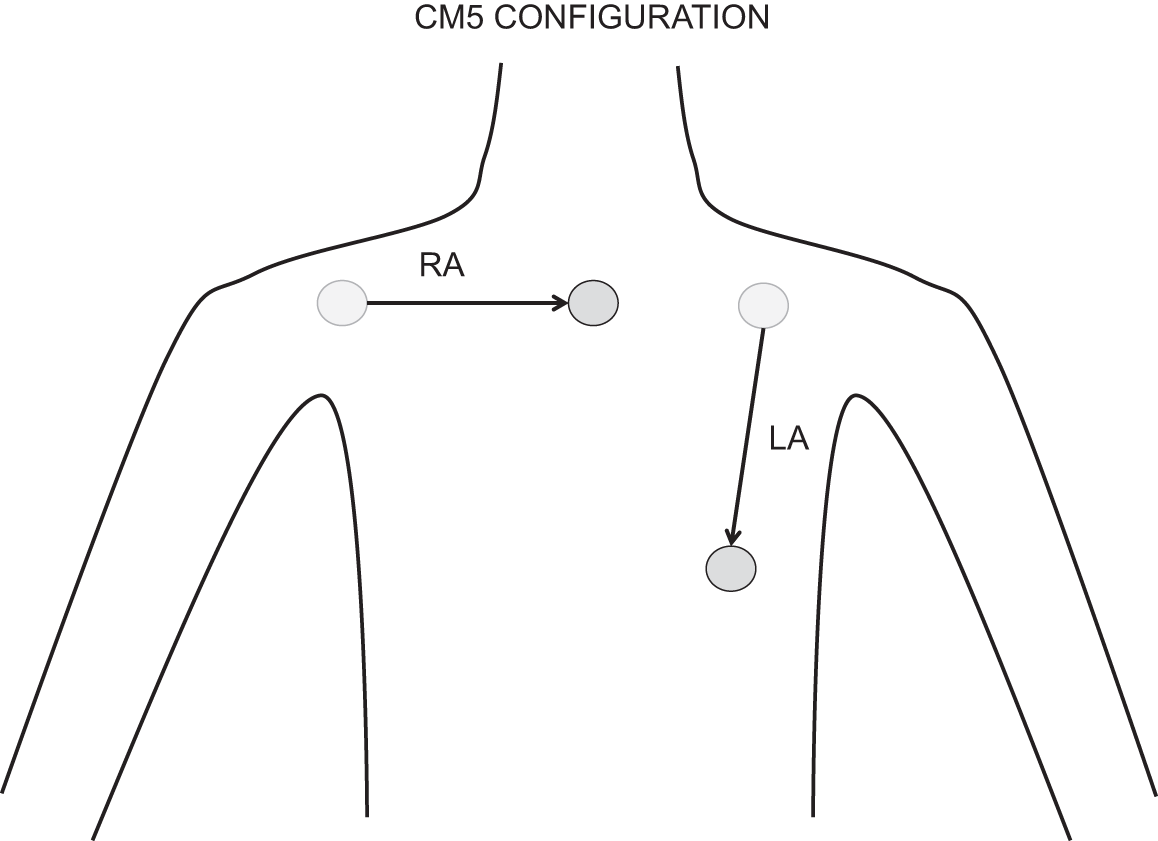
A full 12-lead ECG is unwarranted during routine anaesthesia, as the limb leads alone provide enough information. An alternative configuration of the limb leads is the CM5 Configuration (Central Manubrium V5). In the CM5, the right arm electrode is placed at the suprasternal notch, the left arm electrode at V5 position, and the left leg electrode on the left shoulder or leg to act as a reference point. This configuration lies parallel to the axis of the left ventricle, and is useful for detecting left ventricular ischaemia.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree