Elbow: Extend the elbow and identify the intercondylar line. Palpate the brachial artery pulse medially and the tendon of the biceps brachii muscle laterally. Elevate the shoulder 90 degrees and flex the elbow 90 degrees across patient’s chest to palpate the ulnar groove between the olecranon and the medial epicondyle of humerus where the ulnar nerve is located.
 Wrist: Supinate the forearm and identify the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris. The radial artery runs medial to the radial nerve.
Wrist: Supinate the forearm and identify the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris. The radial artery runs medial to the radial nerve.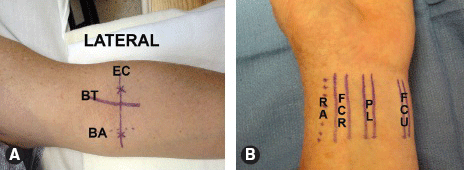
A. Surface anatomy relevant to nerve blocks at the elbow (left arm shown abducted 90 degrees at the shoulder). EC, elbow crease; BT, biceps tendon; BA, brachial artery. B. Surface anatomy relevant to nerve blocks at the wrist (left hand and wrist shown). RA, radial artery; FCR, flexor carpi radialis tendon; PL, palmaris longus tendon; FCU, flexor carpi ulnaris tendon.
US-GUIDED MEDIAN NERVE BLOCK
Median Nerve Block
Approach and Technique
Supinate the arm and place the ultrasound transducer perpendicular to skin.
 Visualize the median nerve in the mid-forearm medial to the radial artery and between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscles.
Visualize the median nerve in the mid-forearm medial to the radial artery and between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor digitorum profundus muscles.
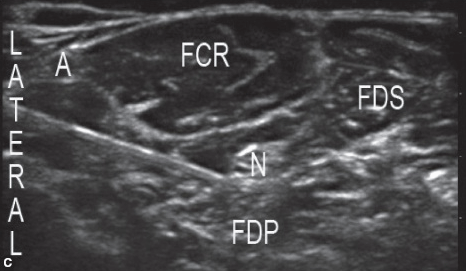
C. Short-axis ultrasound image of the mid-forearm demonstrating sonoanatomy relevant to the median nerve block. A, radial artery; FCR, flexor carpi radialis muscle; FDS, flexor digitorum superficialis muscle; FDP, flexor digitorum profundus muscle; N, median nerve.
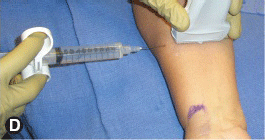
 After sterile skin preparation and local anesthetic skin infiltration, insert the block needle lateral to the transducer and direct it medially toward the median nerve.
After sterile skin preparation and local anesthetic skin infiltration, insert the block needle lateral to the transducer and direct it medially toward the median nerve.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







