Figure 39.1
Entering the lesser sac
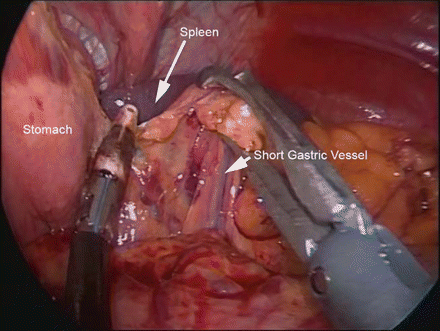
Figure 39.2
Taking down the short gastric vessels
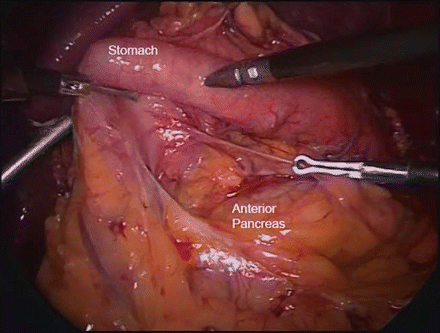
Figure 39.3
Exposing the anterior pancreas
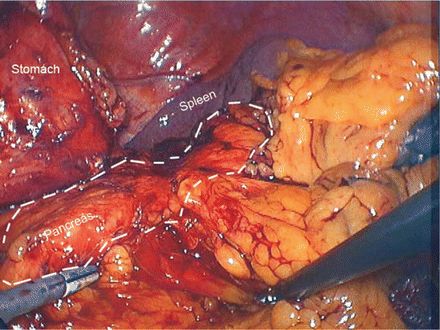
Figure 39.4
The pancreas in situ
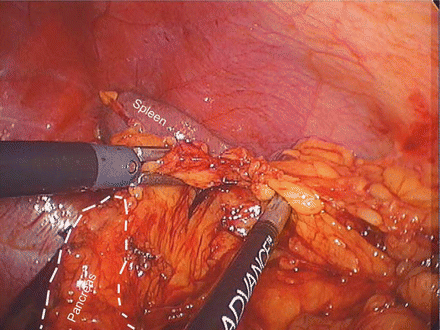
Figure 39.5
Mobilizing the inferior pancreas near the spleen
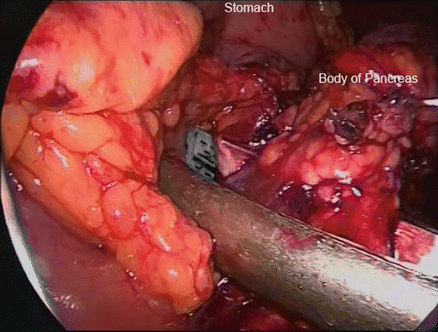
Figure 39.6
Stapling across the pancreas
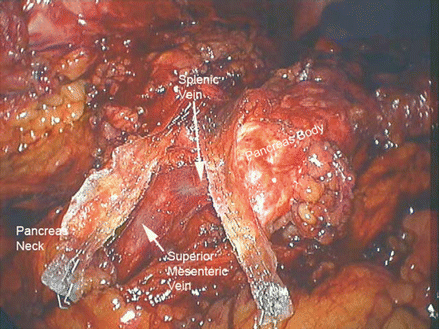
Figure 39.7
The transected pancreas
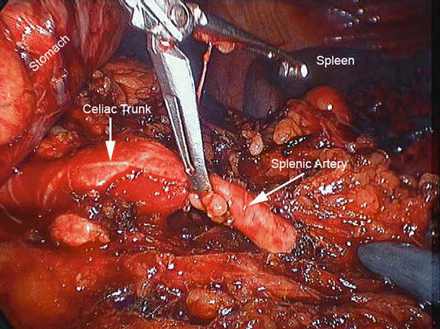
Figure 39.8
Identification of the splenic artery
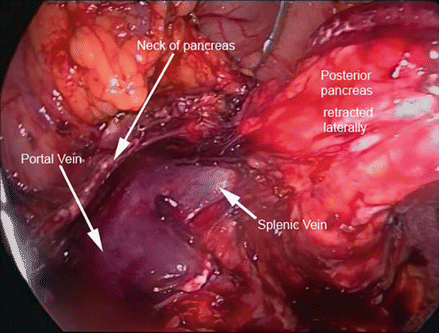
Figure 39.9
Portosplenic confluence exposed
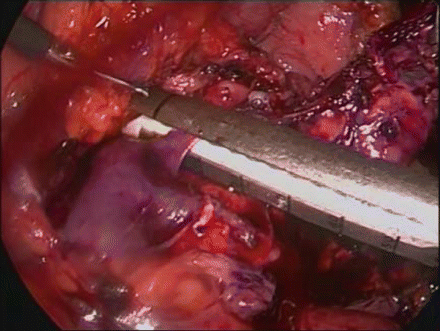
Figure 39.10
Dividing the splenic vein
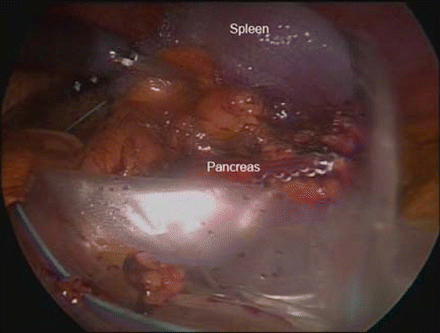
Figure 39.11
The final specimen in the specimen bag
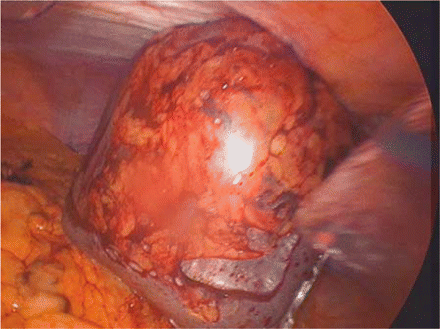
Figure 39.12
The specimen being removed
Postoperative Care
The complication rate following distal pancreatectomy is approximately 30 %. The most common complications encountered are pancreatic leak or fistula (5–29 %) [8, 9], new-onset insulin-dependent diabetes (9 %) [9], intraabdominal abscess (4 %), small bowel obstruction (4 %), and postoperative hemorrhage (4 %) [8]. Postoperative care is targeted to avoid or minimize these complications.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








