3 Core Review Test 3
3-1. Which of the following assessment findings would the nurse anticipate in patients with both right- and left-sided heart failure?
3-2. A patient is admitted to the ICU after attempted drug overdose. He develops generalized muscle rigidity followed by a rhythmic muscle jerking. The nurse observes this activity for 1 minute and pages the physician managing the patient’s care. The activity continues for 10 minutes despite administration of lorazepam 4 mg IV. The next course of action the nurse should anticipate is
3-3. A patient is admitted after exhibiting several neuropsychiatric symptoms including motor coordination difficulties, delayed reaction times, headache, and impaired cognitive skills. During the nurse’s conversations with the family to secure a patient history, the patient’s spouse mentioned that they are in the process of renovating a home that has been in the family for over 50 years. This information suggests that the most likely etiology for this patient’s symptoms is
3-4. Occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery is associated with which of the following complications?
3-5. A patient from the Mediterranean is admitted for unstable angina. The patient reports substernal chest pain 7/10, radiating down his left arm. Vital signs are 136/78 mm Hg, HR 106 beats/min, RR 24/min, temp 98.6° F (37° C). Which of the following medications should be administered with caution to this patient?
3-6. Two hours after open surgical repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm, a patient is hemodynamically stable and mechanically ventilated. Nursing care of the patient at this time should focus on
3-7. A patient with acute exacerbation of COPD is minimally responsive, tachypneic, and tachycardic. Arterial blood gas results include pH 7.20, PaO2 55 mm Hg, and PaCO2 68 mm Hg. The nurse anticipates that the next intervention will be
3-8. A 35-year-old Asian man is admitted with jaundice, elevated liver enzyme levels, malaise, and lack of appetite. His total bilirubin is 34 mg/dL; aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 874 U/L; alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 789 IU/L; prothrombin time (PT) 23 sec; international ratio (INR) 3.2. His HAV IgM is negative; HAV IgG is positive; HCV Ab is negative; HBVsAg is positive; HBVsAb is negative. The probable cause of these findings is
3-9. Which of the following findings indicates that end organ dysfunction has occurred in a patient undergoing treatment for hypertensive crisis?
3-10. A patient is admitted from the operating room after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and has been stable since her craniotomy for left middle cerebral artery aneurysm clipping. On the nurse’s most recent assessment, he notices that the patient has developed new right lower extremity weakness, perseveration, and a rather flat affect. Which of the following interpretations of these new findings will best aid the nurse in planning appropriate care?
3-11. After a motor vehicle crash, a patient undergoes repair of an aortic rupture that extends from just distal to the subclavian artery to 8 cm above the renal artery. During the immediate postoperative period, this patient is at highest risk for development of which of the following?
3-12. Which of the following hemodynamic profiles would the nurse anticipate for a patient with a pulmonary history of COPD?
3-13. A patient diagnosed with acute myocardial infarction suddenly develops hypotension with a blood pressure of 76/58 mm Hg, shortness of breath, and JVD. A loud, high-pitched pansystolic murmur is auscultated. Immediate treatment for the patient would include
3-14. A patient was in the ICU with newly diagnosed diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis and is now ready for discharge. The patient lives alone and is unable to see the numbers on the syringes to self-administer insulin. Which of the following is indicated at this time to decrease the chance of hospital readmission?
3-15. Three days ago, an older patient was admitted to the ICU following abdominal surgery for a perforated bowel. During the past 4 hours, the patient has developed progressive hypotension unresponsive to fluid boluses, has become oliguric, and demonstrates signs of MODS. The nurse’s priority for care now centers on which of the following as the most important intervention in reducing mortality of patients with SIRS and/or MODS?
3-16. A patient with an intra-aortic balloon pump, intubated on mechanical ventilation, is receiving inotropic support with norepinephrine for cardiogenic shock. The patient is hemodynamically stable. Physical assessment findings include bilateral rales, pale dry skin, right radial pulse 1+, left radial pulse absent, right and left dorsalis pedis pulses 1+. Bowel sounds are hypoactive, and urine output is 30 mL/hr. These findings indicate that the intra-aortic balloon is
3-17. A challenge in nursing care of patients undergoing bariatric surgery is adequately meeting the patient’s psychosocial needs. In caring for this patient population, the nurse can anticipate needs related to
3-18. The nurse is conducting discharge teaching for a patient newly diagnosed with COPD. Among the recommendations are smoking cessation, pulmonary rehabilitation therapy, and counseling. At the end of the session, the patient asks if giving up cigarettes will make the COPD “go away.” What is the nurse’s best response?
3-19. After abdominal aortic surgery, a patient develops paralytic ileus. Current vital signs include temperature 36.6° C, heart rate 122/min, sinus tachycardia, BP 82/64 mm Hg, respiratory rate 30/min and shallow owing to abdominal distention. SpO2 is 94% on 4 L oxygen by nasal prongs. Lungs are clear with decreased sounds in the bases. Urine output is 30 mL and 26 mL for the last 2 hours. The patient is restless and complains of abdominal pain. The most likely cause of these findings is
3-20. A 67-year-old with type 2 diabetes is scheduled for an intravenous pyelogram (IVP). To reduce the potentially toxic effects of contrast dye on the kidney, which of the following medical orders should not be implemented until the nurse has conferred with the intensivist?
3-21. An unresponsive patient in the ICU is at end of life. The family has requested that no heroic measures be initiated, that no unnecessary monitoring be used, and that withdrawal of support be initiated. One family member asks why the Bispectral Index Monitor (BIS monitor) is still in use. The nurse’s best response is that
3-22. Which of the following clinical situations places the patient at high risk for the development of pericardial tamponade?
3-23. A patient admitted with necrotizing pancreatitis and has just returned from the operating room where aggressive debridement of peripancreatic tissue was performed. The patient’s postoperative care includes antibiotics, IV fluids, and mechanical ventilation. In managing care for this patient over the next few days, which of the following findings should the nurse recognize as the most reliable indicator of a poor prognosis for this patient?
3-24. A patient comes to ICU following left pneumonectomy for a hilar mass. The patient has stable vital signs and is awake, oriented, intubated, and ventilated on assist-control mode at a rate of 18, tidal volume 8 mL/kg, PEEP +5, and FiO2 .40. The patient’s heart rate and respiratory rate suddenly increase, and his oxygen saturation decreases. The nurse notes that a new central line was placed to the right subclavian site. While increasing the oxygen and preparing for chest tube insertion, the nurse formulates an ongoing plan of care. Which of the following interventions is least likely to be helpful in preventing further pulmonary complications in this patient?
3-25. A combination of furosemide (Lasix) infusion at 8 mg/hr and bumetanide (Bumex) 10 mg fails to produce urine output greater than 25 mL/hr in a hypertensive patient with pulmonary edema. Which of the following interventions does the nurse now anticipate for this patient?
3-26. Anemia and coagulation abnormalities are common hematologic findings in the patient with SIRS/MODS. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings suggests that a patient with SIRS/MODS has now developed one of these coagulation disorders?
3-27. The clinical pathway for a cardiac surgery patient states that today the epicardial pacing wires are to be removed by the nurse. Which of the following conditions would indicate that the nurse should obtain an order to leave the epicardial wires in place?
3-28. A patient with advanced heart failure is deciding whether or not to consent to placement of a ventricular assist device (VAD) and asks for information. Which of the following should the nurse include?
3-29. After ethanol ablation is performed for a patient with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which of the following should the nurse anticipate performing?
3-30. In the early stages of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), nursing interventions primarily focus on
3-31. Patients who are older or malnourished, as well as those with impaired host defense systems or severe illness, are all at increased risk of developing central venous catheter (CVC) infections. Prevention is the most effective means of avoiding infection from this source. Which of the following interventions accurately reflects current guidelines for prevention and management of CVC infections?
3-32. A patient is admitted to the ICU following surgery to remove a bullet from a gunshot wound to the chest. The patient remains intubated on mechanical ventilation and stabilizes with chest tube drainage averaging 75 mL/hr. Two hours later, the nurse notes that the patient’s tidal volumes are decreasing, chest tube output has increased to 300 mL/hr, and BP has decreased from 123/78 to 70/50 mm Hg. After notification of the trauma surgeon, the nurse immediately prepares for
3-33. An ICU patient has become confused and lethargic 5 days after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and aneurysm coil embolization. Which of the following approaches should the nurse anticipate discussing with the acute care nurse practitioner managing this patient’s care?
3-34. An 83-year-old patient with a history of chronic heart failure, longstanding COPD, and osteoarthritis is admitted to the ICU with pneumonia. The patient has undergone tracheostomy and has since failed at three attempts to wean. Although the patient is alert and oriented, he seems too fatigued to assist with the weaning process. Nursing staff are feeling increasingly frustrated in their attempts to help this patient progress. Which of the following would likely help the ICU nursing staff improve outcomes for this patient?
3-35. Following left heart cardiac catheterization, which of the following complications would the nurse be vigilant for?
3-36. A patient with type 1 diabetes is frequently rehospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis. The patient refuses to administer insulin, perform capillary glucose measurement, or follow the diabetic diet since initial diagnosis of the disease. This admission’s initial laboratory results are as follows: glucose 200 mg/dL, pH 6.9, PCO2 25.7 mm Hg, PaO2 94 mm Hg, and bicarbonate 7.0 mEq/L. Which of the following orders should the nurse perform first?
3-37. Which of the following conditions most predisposes the intubated patient to develop ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
3-38. A 12-lead ECG is performed on a patient with wide complex tachycardia demonstrating QS complexes (negative concordance) in all precordial leads. This finding is consistent with which of the following?
3-39. Patients who experience cardiac arrest related to trauma prior to arriving at the hospital rarely survive despite rapid and effective emergency management. Among the interventions designed to improve survival for these patients, which of the following is most important?
3-40. An elevated level of which of the following serum values represents the most specific finding in the diagnosis of perioperative myocardial infarction?
3-41. A patient is in the ICU with septic shock from toxoplasmosis. The patient has a history of AIDS and is intubated and on mechanical ventilation. The patient communicates concern over having not taken antiretroviral treatment since being intubated. The nurse’s best response is
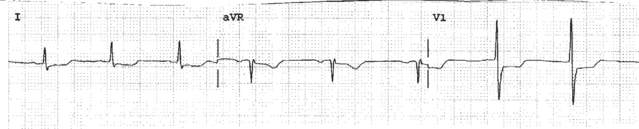
3-42. The 12-lead ECG changes below are indicative of which of the following?
3-43. A trauma surgeon states that nurses do not know how to care for patients with chest tubes and requests that only two specific nurses be assigned to care for his patients when they are in the ICU. The unit’s nursing staff can best manage this situation by
3-44. A patient is recovering from an acute exacerbation of COPD. The physician requests that the patient start ambulating around his room. The nurse knows that this activity
3-45. Biventricular pacemaker implantation is indicated for heart failure associated with which of the following?
3-46. A patient in the ICU is experiencing insomnia and associated agitation. The patient prefers not to take a controlled substance as a sleep aid. In addition to reducing noise and interruptions, which of the following interventions has been shown to be both valuable and feasible in this situation?
3-47. Cardiac catheterization reveals total occlusion of the left anterior descending artery and a filling defect resulting in right ventricular filling during left heart catheterization. Oxygen saturation of the right atrium is 80%, of the right ventricle is 96%, and of the left ventricle is 96%. Which of the following complications associated with acute myocardial infarction do these findings indicate?
3-48. An older patient is admitted after a fall that resulted in a momentary loss of consciousness. The patient’s medications include atenolol, furosemide, digoxin, and paroxetine, and vital signs are BP 110/72 mm Hg, heart rate 56 beats/min, respiratory rate 18 breaths/min. During the nursing history, the patient describes yesterday’s bowel movement as sticky and black in color. Based on these findings, the nurse would initiate interventions aimed at monitoring this patient’s
3-49. The echocardiogram of a patient with acute infectious endocarditis demonstrates tricuspid and pulmonary insufficiency. The patient is intubated and placed on mechanical ventilation and receives propofol and lorazepam for sedation as well as antibiotic therapy. Which of the following is potentially an immediate life-threatening problem for this patient?
3-50. A comatose patient of Gypsy culture is in the ICU and is at the end of life. The nurse should approach the request for organ donation based on which of the following?
3-51. During an initial neurologic assessment, the nurse finds that the patient has a positive Brudzinski’s sign and a positive Kernig’s sign. Otherwise, the patient’s examination is nonfocal. Since the lumbar puncture performed earlier showed high protein and low glucose in the CSF, the nurse’s most appropriate action at this time is to
3-52. Which of the following findings best indicates that fluid resuscitation for hypovolemic shock has been appropriate?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>