1 Core Review Test 1
1-1. A patient admitted with shortness of breath demonstrates the following findings: temperature 36.8° C, HR 120/min sinus tachycardia, BP 130/76 mm Hg, RR 36/min with SpO2 91%. Breath sounds reveal inspiratory crackles and rhonchi in all lung fields. The chest x-ray report states that there are Kerley B lines, enlargement of the peribronchial hilar spaces, and enlarged cardiac silhouette. These findings are consistent with which of the following?
1-2. A research study is being conducted in the ICU and telemetry units to look at the effectiveness of steroid use prior to cardiac catheterization. A 56-year-old telemetry patient is approached by one of the research staff; the patient’s nurse, outside the room, overhears their conversation. The staff member asks the subject if he would like to enroll in the study because it is a quick way to make $100. The patient asks whether any risk is involved, and the staff member says, “Not really. All you have to do is sign this form.” How should the patient’s nurse respond?
1-3. A patient is hospitalized for severe fractures of the pelvis and left femur. Two hours after the initial patient assessment, the nurse notes the following findings: increased anxiety and confusion, BP unchanged at 148/84 mm Hg, HR increased from 120 to 146/min, respiratory rate increased from 18 to 44/min. Pulmonary artery pressures are 55/28 mm Hg, and cardiac output is decreased from 4 to 2.3 L/min. The nurse’s intervention at this point should be to
1-4. A patient undergoes emergency CABG surgery after failed thrombolysis and a percutanous coronary intervention in which coronary artery dissection occurred. Prior to surgery, the patient was alert and able to give verbal consent. Mediastinal and pleural chest tubes are present with moderate drainage. Moderate oozing is also present at the sternotomy and saphenous vein graft incisions and at the right groin sheath site. The patient has a PA catheter, an NG tube, and a urinary catheter in place. Frequent assessments by the nurse for this patient should include which of the following?
1-5. For a patient admitted to the hospital after a motor vehicle crash, which of the following assessment components would the critical care nurse expect to perform at the bedside immediately upon arrival?
1-6. A patient in the ICU was admitted for acute coronary artery syndrome. Which of the following leads is recommended for ST segment monitoring?
1-7. Which of the following vasopressors is indicated in low cardiac output syndrome when the desired effect is vasoconstriction without tachycardia?
1-8. A patient with urosepsis was admitted to the ICU 12 hours ago, has received 6 L of fluid thus far, and is receiving levophed to maintain her systolic BP >90 mm Hg. She is on assist-control ventilation with a rate of 12, tidal volumes of 8 mL/kg, PEEP of +5, and FiO2 of .50. Over the past 2 hours, her oxygen saturation has been slowly decreasing from 99% to 90% despite increasing her FiO2 to .80. Her most recent ABG shows a pH of 7.30, PaCO2 of 55 mm Hg, and PaO2 of 60 mm Hg. Her pulmonary pressures are increasing, and her static pressure is now 40. What ventilator changes does the nurse anticipate?
1-9. A patient is admitted to the ICU after sustaining a concussion and blunt abdominal trauma to the right upper quadrant in a domestic dispute. The patient’s vital signs are BP 145/86 mm Hg, pulse 86 beats/min, respiration 15 breaths/min, and temperature 98.8° F. The nurse is monitoring the patient’s bowel sounds, abdominal tenderness, and abdominal girth frequently. Which of the following laboratory parameters is especially important for the nurse to closely monitor for bleeding in this patient?
1-10. A patient is admitted for elective craniotomy and clipping of a posterior communicating artery aneurysm. On the initial ICU assessment, the nurse notes that the patient’s Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is 15 with no focal weakness. The patient has a large, nonreactive pupil as well as ptosis in the left eye. The nurse’s best course of action at this point would be to
1-11. Approximately 3 minutes after the first CRRT treatment is begun, a patient complains of severe back pain and itching. The patient’s vital signs are BP 84/50 mm Hg, HR 115 beats/min, RR 26/min. The nurse’s initial intervention for this patient would be to
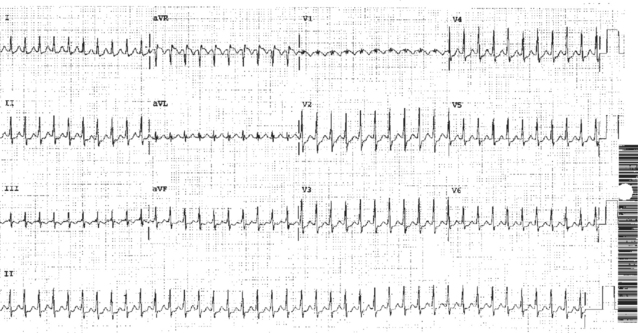
1-12. The alarm on a patient’s monitor sounds, and the nurse immediately responds to assess the patient. The patient denies chest pain but complains of palpitations. The nurse places oxygen on the patient and obtains the following vital signs: BP 120/70 mm Hg and respiratory rate 22/min. The nurse then obtains the 12-lead ECG below. The most appropriate immediate intervention for the nurse would be to
1-13. Bedside transesophageal echocardiography reveals a dissecting aortic aneurysm with pericardial effusion in a patient with a blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg. Prior to transferring the patient to the operating room, which of the following does the nurse need to prepare for?
1-14. After a patient has received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), one of the most common psychological problems the patient may experience is
1-15. A patient admitted for acute alcohol ingestion was intubated by paramedics at the scene because of a decreased level of consciousness. The paramedics reported that the patient vomited a large amount of emesis during the intubation. On admission to the ICU, the patient’s vital signs are as follows: temperature 38.5° C, HR 120/min, BP 90/60 mm Hg, RR 28/min, SaO2 94% on FiO2 100%. A chest x-ray shows infiltrates in the patient’s right lower lobe. Which of the following interventions should the critical care nurse anticipate?
1-16. Recent research has found that African Americans experiencing myocardial infarction are likely to delay treatment if they are single, widowed, or divorced, because they do not view their symptoms as life-threatening or serious. A nurse is now planning care for a 56-year-old African-American patient who delayed coming into a small community hospital for chest pain and experienced a myocardial infarction without the opportunity to receive thrombolytics. The nurse’s plan of care for this patient should include
1-17. A patient is admitted to the critical care unit from the general surgical floor after an episode of vomiting. The patient developed respiratory distress secondary to aspiration pneumonia and required intubation for refractory hypoxia and airway management. During the past week, the patient has remained hypoxic despite aggressive pulmonary support and has developed acute tubular necrosis and hepatic failure. To establish appropriate priorities of care for this patient, the nurse needs to plan care for a patient with which of the following conditions?
1-18. A patient admitted 2 weeks ago for bilateral flail chest injuries associated with a motor vehicle collision had chest tubes inserted and has been intubated and mechanically ventilated throughout that period. His left chest tube demonstrates persistent bubbling during inspiration and expiration, although his breath sounds are clear bilaterally and the drainage system is working properly. Which of the following interventions should the critical care nurse consider next?
1-19. The critical care nurse is performing peritoneal dialysis on a patient with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Following the inflow period, the patient complains of severe shoulder pain. The critical care nurse should immediately
1-20. A patient is admitted following involvement in a multi-vehicle collision. The patient’s urine output has increased from 125 mL to 1000 mL over the last 2 hours. Which of the following is the most important assessment the nurse should make at this time?
1-21. A patient is intubated for acute respiratory failure. The patient has no history of cardiac disease, and there is no evidence of peripheral edema. Upon admission to the ICU, diagnostic testing reveals the following:
1-22. A patient recently treated for deep vein thrombosis is now admitted to the ICU. The patient is pale and complains of dizziness, chest pain, and shortness of breath. During the review of medications, the nurse learns that the patient has been on heparin therapy. Which of the following laboratory tests would be most important for determining whether this patient is experiencing heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
1-23. A 42-year-old man is admitted to the ICU with severe abdominal pain, elevated lipase levels, and no prior history of alcoholism. A tentative diagnosis of pancreatitis has been made. The patient states that he never wants to suffer this way again. How can the nurse best assist this patient in better understanding his diagnosis to meet his goal?
1-24. Pulmonary edema is most likely to develop when
1-25. A patient who has been hospitalized for several weeks with a severe pelvic fracture is readmitted to the ICU with hypotension, chest pain, and shortness of breath. His BP is now 88/54 mm Hg, down from 128/77 mm Hg in the emergency department; pulse is 74 beats/min, and respiratory rate is 28 breaths/min. The patient does not exhibit edema, pulses are 2+, and extremities are warm. The most likely cause of this patient’s hypotension is
1-26. A patient admitted to the ICU after endovascular repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) has the following assessment findings: BP 120/74 mm Hg, HR 90/min, RR 20/min, temperature 36° C. Distal pulses are 2+, capillary refill is 2 seconds, and the groin site demonstrates no evidence of hematoma. Urine output is 20 mL/hr for 2 hours. The most likely cause of decreased urine output is
1-27. A patient is in the ICU after undergoing a gastric resection for stomach cancer and has been started on a regular diet prior to transfer out of the unit. Within minutes of eating, the patient develops diaphoresis, weakness, cramping, and palpitations, BP is 102/70 mm Hg, pulse is 96 beats/min, and respirations are 22 breaths/min. Which of the following conditions best explains these clinical findings?
1-28. An 88-year-old woman is admitted to the ICU with electrolyte imbalance, malnutrition, and chest pain. Upon receiving the patient from the emergency department, the ICU nurse notices the residue from a tape mark across the patient’s mouth, which was documented in the patient’s ED assessment. After the two nurses discuss this finding, what should be considered as the next best course of action?
1-29. A patient who is 32 weeks’ pregnant is admitted with pre-eclampsia and generalized edema. BP is 210/128 mm Hg, pulse is 120 beats/min, RR is 36/min. The chest x-ray shows evidence of pulmonary edema. Prior to transfer to the ICU, 40 mg of furosemide (Lasix) is administered to the patient. Which of the following medications would be used to reduce blood pressure and prevent potential harm to the fetus?
1-30. A patient in the ICU is intubated and mechanically ventilated on the following settings: tidal volume 600 mL, rate 12/min, FiO2 70%, PEEP 15 cm H2O. The peak inspiratory pressure is 50 cm H2O, and the patient’s respiratory rate is 12/min. Arterial blood gas values include pH 7.25, PaO2 60 mm Hg, PaCO2 48 mm Hg. Which of the following findings would best indicate clinical improvement in this patient?
1-31. In caring for a patient who is mechanically ventilated, the critical care nurse will best implement evidenced-based recommendations for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and possible development of bacteremia and sepsis by
1-32. Upon arrival to the critical care unit after coronary artery bypass graft surgery, the patient has a BP of 180/110 mm Hg, a heart rate of 70 beats/min 100% paced, a RAP of 6 mm Hg, a PAD of 10 mm Hg, a temperature of 36° C, and cardiac output of 3.5 LPM. Urine output for the first hour is 60 mL. Which of the following interventions should the nurse perform first?
1-33. A 30-year-old patient with longstanding asthma was admitted to the ICU with a severe asthma attack. Her work of breathing has been increasing, and her most recent ABG results on 40% facemask are pH 7.25, PCO2 65 mm Hg, PO2 60 mm Hg, and HCO3 25 mEq/L. Based on these findings, which of the following interventions should the critical care nurse anticipate?
1-34. Ventilator-associated pneumonias (VAP) result in approximately 6 more days in the ICU, and $10,000 to $40,000 per episode in costs. Your facility has decided to focus on decreasing VAP. Which of the following interventions would provide the farthest-reaching impact on this health problem?
1-35. The patient admitted with a presumptive diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction has an insulin drip infusing. Over the past 30 minutes, the patient has become agitated and irritable. Which of the following should the nurse do first?
1-36. A patient about to receive a bone marrow transplant is in strict isolation and expressing feelings of anxiety. Nursing measures appropriate to this situation include
1-37. The nurse should immediately perform which of the following interventions for a patient with chest pain, hypotension, and tachycardia at a rate of 180 beats/min?
1-38. During a staff meeting, the unit-based performance improvement nurse provides data on stress-related mucosal disease (SRMD) in the ICU. Data for 3 months suggest that, on average, 20 of the monthly census of 100 patients are developing SRMD. The nurse asks her colleagues for suggestions to decrease the incidence of SRMD. One good suggestion would be to
1-39. After cardiac catheterization with percutaneous balloon angioplasty, a patient develops a paradoxical pulse. The most likely cause for this finding is
1-40. A postoperative abdominal surgery patient weighing 700 lb (318 kg) develops acute onset of dyspnea and chest pain. Arterial blood gas values are pH 7.35, PaO2 is 74 mm Hg, PaCO2 is 30 mm Hg, and O2 is saturation 90%. Chest x-ray demonstrates an enlarged cardiac silhouette, a prominent pulmonary artery, and mild right pleural effusion. The 12-lead ECG demonstrates T wave inversions in the anterior leads. These findings suggest that this patient has most likely developed which of the following?
1-41. A patient with chronic renal failure presents to the ED with severe itching, abdominal cramps, nausea, and diarrhea. The patient’s serum calcium is 6.2 mg/dL. Which of the following needs to be administered for management of this patient?
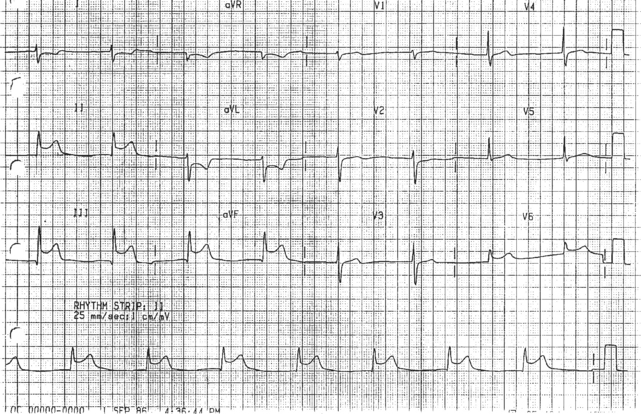
1-42. The 12-lead ECG above is obtained on a patient experiencing chest pain. The nurse administers 1/150 grains of sublingual nitroglycerin, and the patient’s BP drops from 130/80 mm Hg to 80/50 mm Hg. The most likely cause of the decrease in blood pressure for this patient is
1-43. A patient had an upper esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) 30 minutes ago and is drowsy. As the patient is slowly waking up, he asks, “Can I have a drink of water?” The nurse’s best response would be to say
1-44. A multiple trauma patient with a grade IV liver laceration is re-admitted to the ICU from the operating room after having the liver packs replaced for the third time. The patient has been on mechanical ventilation for 5 days and maintenance of the ventilator equipment is now being considered. Which of the following measures for prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia is indicated at this time?
1-45. When a patient with an implanted cardioverter defibrillator develops rapid atrial fibrillation that results in inappropriate delivery of defibrillation shocks, the nurse’s first intervention should be to
1-46. A patient has been receiving intravenous steroids to treat an acute exacerbation of asthma. While previously alert and oriented, this morning the patient is obtunded, and morning labs reveal a serum glucose of 624 mg/dL with no other notable findings. In planning care for this patient, which of the following conditions should the nurse now anticipate needing to manage?
1-47. Classic echocardiographic features of diastolic dysfunction in patients diagnosed with heart failure would include which of the following?
1-48. A nurse in a 16-bed ICU that is managed with a shared governance model is currently the chair of a multidisciplinary committee that evaluates use of medical devices for attriutes such as unit costs, type, infection rate, and malfunction rate. The committee is notified that a new cardiologist coming in a few months will be implanting cardioverter-defibrillator devices, so the hospital would like the committee to develop a tool to be used to evaluate outcomes related to this device, similar to a registry (log of positive and negative outcomes). As the leader of this multidisciplinary group, how should the nurse proceed to investigate this device?
1-49. An ICU nurse caring for a patient admitted with severe abdominal discomfort and fatigue notes that the patient tested positive for Helicobacter pylori and has a history of cigarette smoking. The patient develops nausea and abdominal tenderness. His vital signs are BP 123/80 mm Hg, pulse 89 beats/min, respirations 15 breaths/min. Within 15 minutes, the patient vomits, and his emesis contains coffee grounds. His vital signs are BP 100/68 mm Hg, pulse 120 beats/min, respirations 24 breaths/min. Which of the following medical orders for this patient merits the nurse’s immediate attention?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree