Board Simulation: Neonatology
Elumalai Appachi
QUESTIONS
1. A 4-week-old male infant presents with fever and irritability for 3 days. On examination he lies motionless and has an erythematous rash, bullae, and peeling of the skin. He has circumoral erythema and has crusting and fissuring around the mouth, eyes, and nose (Fig. 23.1). Which of the following is true regarding the diagnosis and management of this illness?
a) It is almost always acquired in utero.
b) It is usually associated with pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, or impetigo.
c) Fluid restriction is required to prevent bullae formation.
d) The skin lesions heal and leave a pigmented whorllike pattern.
e) Ampicillin is the drug of choice.
View Answer
Answer
The answer is b. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a toxin-mediated complication of Staphylococcus aureus infection, characterized by bullous impetigo, generalized scarlatiniform erythematous rash, and systemic manifestations. The skin is extremely tender and the affected infant barely moves as movement aggravates the pain. Conjunctivitis, pharyngitis, and pneumonia are common associated features. The disease is more common in infants and young children, and the foci of infection include the nasopharynx, umbilicus, urinary tract, superficial abrasion, and rarely, the blood. The intact bullae contain sterile fluid (since toxin-mediated) but cultures should be obtained from the blood and all suspected sites of localized infection. Separation of the epidermis at the site of pressure on the skin (Nikolsky sign) is common and at times large areas of the epidermis peel away easily. Systemic therapy with semisynthetic penicillinaseresistant penicillin is the drug of choice. Recovery is rapid and healing occurs without scarring.
2. This full-term infant was born to a 24-year-old primigravida. During routine postnatal examination you notice this abnormality (Fig. 23.2). All of the following are true regarding this condition except:
a) Chromosomal analysis should be performed on the infant and parents.
b) The infant may develop moderate to severe learning disability.
c) The risk of having this condition in future pregnancies is 50%.
d) An echocardiogram should be performed on this infant.
e) Thyroid hormone abnormality is commonly found in this condition and therefore thyroid function needs to be evaluated.
View Answer
Answer
The answer is c. The picture shows Brushfield spots, or speckled irises, which are one of the presenting features of Down syndrome (trisomy 21). Other common features include hypotonia, mental and growth retardation, cardiac malformations, midgut anomalies, and thyroid abnormalities. The incidence of Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is 1/600 to 800 live births. Approximately 4% to 5% of children with Down syndrome have a translocation involving the chromosome 21. One of the parents is a translocation carrier in about half of the cases. Hence it is important to get chromosomal analysis done in the child and parents. The risk for future pregnancies is much lower than 50%.
3. The parents of this neonate are concerned about the birthmark (Fig. 23.3). All of the following are true statements about this neonate and her condition except:
a) The birthmark will disappear slowly as she grows older.
b) Imaging of her brain is part of the initial workup.
c) She is at risk of developing a seizure disorder.
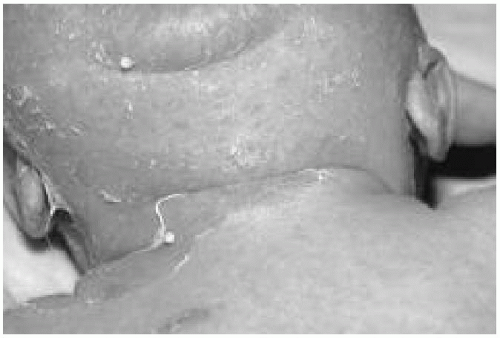 Figure 23.1 The infant in question 1. See explanation of question 1 for details. (See color insert.) |
d) She may develop moderate to severe learning disability.
e) Future pregnancies are not at increased risk.
View Answer
Answer
The answer is a. Sturge-Weber syndrome is a sporadic condition characterized by facial port-wine stain, seizures, hemiparesis, and moderate-to-severe mental retardation. The port-wine stain has to be differentiated from the salmon patch, a benign condition. Port-wine stains do not regress. The facial nevus is usually unilateral and tends to involve the upper face, but occasionally may involve the whole upper half of the body. Ocular manifestations include buphthalmos and glaucoma of the eye on the side of the port-wine stain. Tonic-clonic seizures, which may be intractable, develop during infancy. Mental retardation develops in more than 50% of the cases. X-ray of the skull shows a characteristic calcification “railroad pattern” and a computed tomography (CT) scan of the brain shows ipsilateral atrophy of the brain. Functional hemispherectomy or lobectomy has shown to control the seizures and delay the development of mental retardation. The most effective therapy for the port-wine stain is flash-lamp-pumped pulsed dye laser.
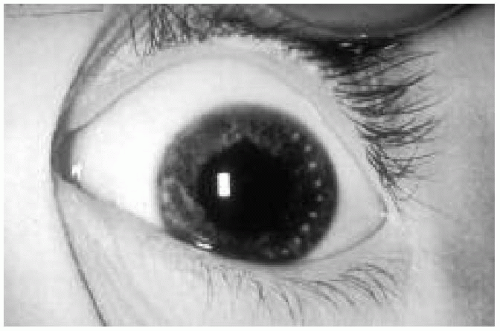 Figure 23.2 The infant in question 2. See explanation of question 2 for details. (See color insert.) |
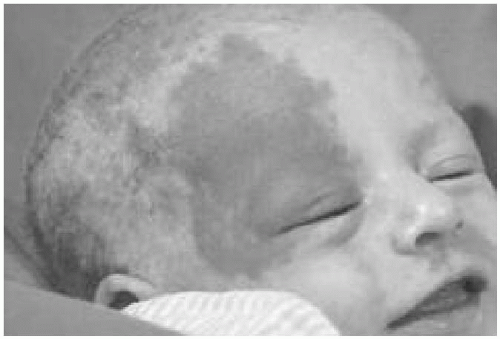 Figure 23.3 The “birthmark” of the neonate in question 3. See explanation of question 3 for details. (See color insert.) |
4. Examination of a neonate reveals this physical feature (Fig. 23.4). The following are true regarding his condition except:
a) An echocardiogram should be performed to evaluate for any associated cardiac anomalies.
b) He may develop pancytopenia.
c) Chromosomal studies should be performed
d) Future pregnancies are not at risk
e) He may have an increased predisposition to malignancies.
View Answer
Answer
The answer is d. Fanconi anemia is an autosomal-recessive condition characterized by physical abnormalities including short stature, café au lait spots, and abnormalities in hands and arms. The upper limb abnormalities include absent thumb and absent radius. Pancytopenia develops because the marrow is usually aplastic. A small percentage of patients may have associated internal organ
abnormalities including heart defects. Children with this disorder are at increased risk for developing leukemia and other malignancies. Chromosomal breakage studies are required because chromosomal breaks occur; parents need genetic counseling for future pregnancies.
abnormalities including heart defects. Children with this disorder are at increased risk for developing leukemia and other malignancies. Chromosomal breakage studies are required because chromosomal breaks occur; parents need genetic counseling for future pregnancies.
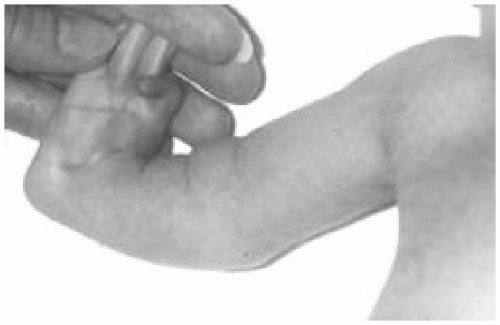 Figure 23.4 The physical feature of the neonate in question 4. See explanation of question 4 for details.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|


