Important surface landmarks to identify include the most cephalad portions of the medial malleolus (MM), lateral malleolus (LM), and the Achilles tendon posteriorly. The sural nerve is located in the subcutaneous tissue between the LM and Achilles tendon. Have the patient dorsiflex the great toe to identify the extensor hallucis longus (EHL) tendon. The tendon of tibialis anterior lies medial to the EHL, and the dorsalis pedis artery is typically palpable between these two tendons. The deep peroneal nerve innervates the webspace between the first and second toes. It lies deep to the extensor retinaculum between the two tendons and is closely associated with the dorsalis pedis artery.
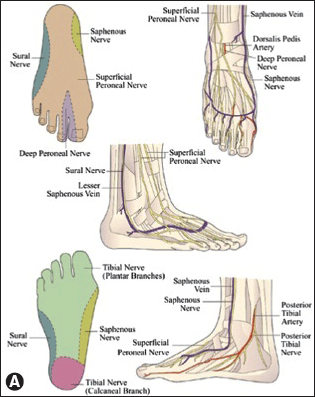
A. Anatomic landmarks. From Clanton TO, Loncarich DP. Ankle block. In: Chelly JE. Peripheral nerve blocks: A color atlas. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009: 158, with permission.
Approach and Technique
US-Guided Tibial Nerve Block
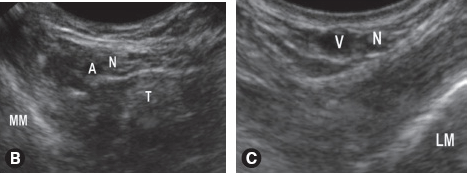
 Place the transducer cephalad to the MM and image the posterior tibial artery in short axis. The nerve will appear immediately posterior to the artery. Injection of 5 mL of local anesthetic around the nerve will result in reliable anesthesia.
Place the transducer cephalad to the MM and image the posterior tibial artery in short axis. The nerve will appear immediately posterior to the artery. Injection of 5 mL of local anesthetic around the nerve will result in reliable anesthesia.
US-GUIDED ANKLE BLOCK
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







