CHAPTER 7 Face and neck nerve blocks
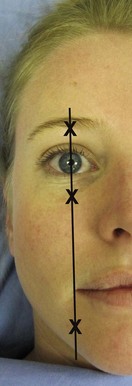
Nerve blocks in the head and face are useful for the repair of lacerations and for scrubbing and debriding ‘roasties’. Nerve blocks in this region are less painful to the patient than local infiltration and they do not distort the anatomy. The supraorbital nerve, the infraorbital nerve and the mental nerve all exit their foramina along a line that can be drawn 25 mm lateral to the midline of the face through the pupil and the labial angle (Fig. 7.1).
Supraorbital and supratrochlear nerve blocks
Ultrasound can also be used to identify the precise location of the supraorbital foramen.
Technique
Lateral or inferior approach
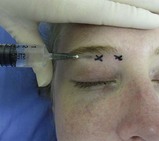
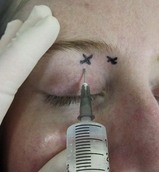
If performed from the side of the supraorbital foramen (Figs 7.2, 7.3):
Medial approach
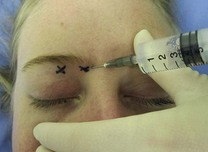
If the block is performed from the area of the supratrochlear nerve (Fig. 7.4):
Ultrasound assistance
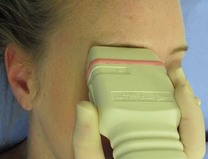
Ultrasound can be used to define the exact position of the supraorbital foramen (Figs 7.5, 7.6A&B). This position can then be marked on the skin and the procedure performed blind (an ultrasound-aided technique) or the out-of-plane approach can be used to advance the needle to a point just superficial to the foramen before injecting local anaesthetic (an ultrasound-guided technique).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree