Chapter 42 Acute Renal Failure
3 How is ARF classified?
The main categories are prerenal, intrarenal or parenchymal, and postrenal or obstructive (Table 42-1).
Table 42-1 Differential diagnosis of acute renal failure
| Prerenal | Postrenal | Parenchymal |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Ureter | Glomerular |
| Impaired cardiac function | Bladder | Interstitial |
| Vasodilation | Urethra | Allergic interstitial nephritis |
| Renal vascular obstruction | Vascular | |
| Hepatorenal syndrome | ATN |
ATN, Acute tubular necrosis.
5 What are the implications of urinary electrolytes in the differential diagnosis of ARF?
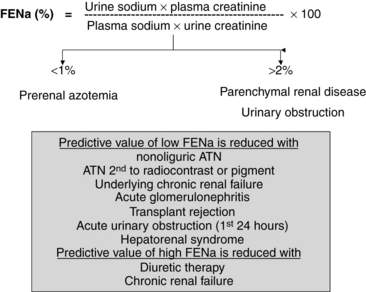
The determination of urine electrolyte and creatinine concentrations may be helpful in the differential diagnosis of ARF. When used with serum values, urinary diagnostic indexes can be generated. Understanding the concepts behind the interpretation of these indexes is easier and better than trying to remember specific numbers. Quite simply, if the tubule is working well in the setting of decreased GFR, tubular reabsorption of sodium and water is avid, and the relative clearance of sodium to creatinine is low. Conversely, if the tubule is injured and cannot reabsorb sodium well, the relative clearance of sodium to creatinine is not low. Therefore, with prerenal azotemia, the ratio of the clearance of sodium to the clearance of creatinine, which is also called the fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) (FENa = [Urinary sodium]/[Urinary creatinine] × [Plasma creatinine]/[Plasma sodium] × 100), is typically less than 1.0, whereas with parenchymal or obstructive causes of ARF, the FENa is generally greater than 2.0 (Fig. 42-1).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree