Point-of-care ultrasound: the application of ultrasound by the bedside clinician for the purpose of answering diagnostic questions or guiding procedures
 Of great value in the ICU, where the patient’s status changes rapidly and diagnostic and therapeutic applications of ultrasound are necessary without delay
Of great value in the ICU, where the patient’s status changes rapidly and diagnostic and therapeutic applications of ultrasound are necessary without delay
Main Variables that Determine Ultrasound Image Quality
 Frequency
Frequency
 Largely determined by transducer selection
Largely determined by transducer selection
 High-frequency transducers provide excellent resolution but limit the depth at which structures can be viewed.
High-frequency transducers provide excellent resolution but limit the depth at which structures can be viewed.
 For structures close to the body surface → high-frequency transducer
For structures close to the body surface → high-frequency transducer
 For deep structures → low-frequency transducer
For deep structures → low-frequency transducer
 Depth
Depth
 Increasing depth allows the user to view more structures.
Increasing depth allows the user to view more structures.
 Increased depth causes reduction in resolution.
Increased depth causes reduction in resolution.
 Gain
Gain
 Increasing gain increases the intensity, or brightness, of the image
Increasing gain increases the intensity, or brightness, of the image
 Under-gained images are too dark to interpret
Under-gained images are too dark to interpret
 Over-gained images are too bright to interpret
Over-gained images are too bright to interpret
Ways to Manipulate the Ultrasound Transducer
 Move
Move
 The transducer can be moved to a different location on the body
The transducer can be moved to a different location on the body
 Tilt
Tilt
 Pitch: tilt up and down, cephalad/caudad, or in the sagittal plane
Pitch: tilt up and down, cephalad/caudad, or in the sagittal plane
 Yaw: tilt side to side, right/left, or in the transverse plane
Yaw: tilt side to side, right/left, or in the transverse plane
 Rotate about an axis
Rotate about an axis
To achieve optimal imaging, the user must alter only the location or the tilt or the rotation at one time.
Focused Echocardiography
Bone effectively blocks the transmission of ultrasound waves; so the user must employ a small-headed transducer and anatomic “windows” to view the heart:
1. Parasternal
2. Apical
3. Subcostal
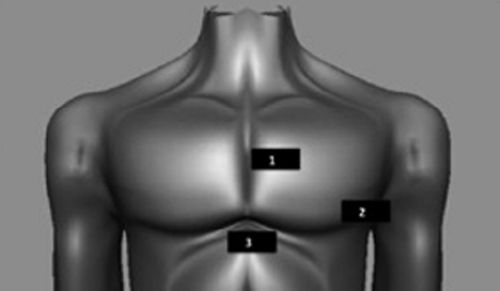
Reprinted with permission from authors, Ferrada P, Murthi S, Anand RJ, et al. Transthoracic focused rapid echocardiographic examination: real-time evaluation of fluid status in critically ill trauma patients. J Trauma. 2011;70(1):56-62.
Goals of Focused Transthoracic Echocardiography
Answer specific clinical questions:
 Left ventricle
Left ventricle
 Size/dilation
Size/dilation
 Systolic function
Systolic function
 Hyperdynamic, normal, depressed, or severely depressed
Hyperdynamic, normal, depressed, or severely depressed
 Right ventricle
Right ventricle
 Size/dilation
Size/dilation
 Systolic function
Systolic function
 Normal or depressed
Normal or depressed
 Pericardial effusion: present or absent
Pericardial effusion: present or absent
 Evidence of tamponade: right atrial and ventricular collapse, plethoric IVC
Evidence of tamponade: right atrial and ventricular collapse, plethoric IVC
 Valves
Valves
 Gross appearance on 2D imaging
Gross appearance on 2D imaging
 Color Doppler for regurgitation
Color Doppler for regurgitation
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


